Overview
Plantar warts are small, rough growths on the feet. They usually show up on the balls and heels of the feet, the areas that bear the most pressure. This pressure may also cause a wart to grow inward beneath a hard, thick layer of skin (callus).
Plantar warts are caused by HPV. This virus enters through tiny cuts or breaks on the bottom of the feet.
Most plantar warts aren't a serious health concern and often go away without treatment, especially in children under 12. To get rid of them sooner, you can try self-care treatments or see your health care provider.
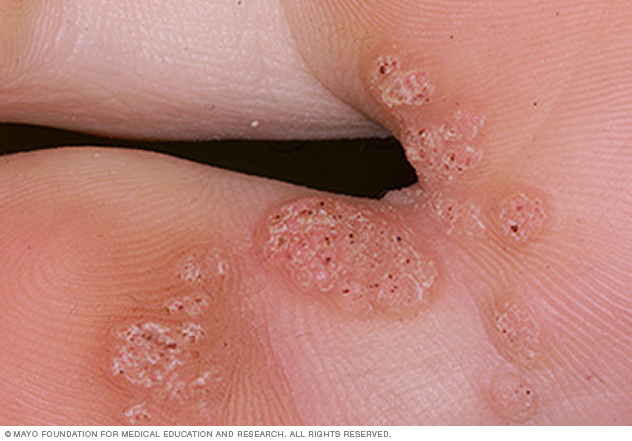
Symptoms
Plantar wart signs and symptoms include:
- A small, rough growth on the bottom of your foot, usually at the base of the toes or on the ball or heel
- On brown and Black skin, the growth may be lighter than unaffected skin
- Hard, thickened skin (callus) over a spot on the skin, where a wart has grown inward
- Black pinpoints, which are small clotted blood vessels commonly called wart seeds
- A cluster of growths on the sole of the foot (mosaic warts)
- A growth that interrupts the normal lines and ridges in the skin of your foot
- Pain or tenderness when walking or standing
When to see a doctor
See your health care provider for the growth on your foot if:
- The growth is bleeding, painful or changes in shape or color
- You've tried treating the wart, but it persists, multiplies or comes back after clearing for a time (recurs)
- Your pain interferes with your activities
- You also have diabetes or poor feeling in your feet
- You also have a weak immune system because of immune-suppressing drugs, HIV/AIDS or other immune system disorders
- You aren't sure if the growth is a wart
Causes
Plantar warts are caused by an infection with HPV in the outer layer of skin on the soles of the feet. The warts develop when the virus enters through tiny cuts, breaks or weak spots on the bottom of the foot. If left untreated, warts can last from a few months to 2 years in children, and several years in in adults.
HPV is very common, and more than 100 kinds of the virus exist. But only a few of them cause warts on the feet. Other types of HPV are more likely to cause warts on other areas of your skin or on mucous membranes.
Transmission of the virus
Each person's immune system responds differently to HPV. Not everyone who comes in contact with it develops warts. Even people in the same family react to the virus differently.
The HPV strains that cause plantar warts aren't highly contagious. So the virus isn't easily spread by direct contact from one person to another. But it thrives in warm, moist places, so you might get the virus by walking barefoot around swimming pools or locker rooms. If the virus spreads from the first site of infection, more warts may grow.
Risk factors
Anyone can develop plantar warts, but this type of wart is more likely to affect:
- Children and teenagers
- People with weak immune systems
- People who have had plantar warts before
- People who walk barefoot in areas where a wart-causing virus is common, such as locker rooms and swimming pools
Complications
When plantar warts cause pain, you may alter your normal posture or gait — perhaps without realizing it. Eventually, this change in how you stand, walk or run can cause muscle or joint discomfort.
Prevention
To help prevent plantar warts:
- Avoid direct contact with warts. This includes your own warts. Wash your hands carefully after touching a wart.
- Keep your feet clean and dry.
- Wear sandals or other foot protection when walking around swimming pools, in locker rooms or in gym showers.
- Don't pick at or scratch warts.
- When using an emery board, pumice stone or nail clipper on your warts, choose one that you don't use on your healthy skin and nails.
Diagnosis
A health care provider usually diagnoses a plantar wart by looking at it or cutting off the top layer with a scalpel and checking for dots. The dots are tiny clotted blood vessels. Or your health care provider might cut off a small section of the growth and send it to a lab for testing.
Treatment
Most plantar warts are harmless and go away without treatment, though it may take a year or two in children, and even longer in adults. If you want to get rid of warts sooner, and self-care approaches haven't helped, talk with your health care provider. Using one or more of the following treatments may help:
-
Freezing medicine (cryotherapy). Cryotherapy is done in a clinic and involves applying liquid nitrogen to the wart, either with a spray or a cotton swab. This method can be painful, so your health care provider may numb the area first.
The freezing causes a blister to form around your wart, and the dead tissue sloughs off within a week or so. Cryotherapy may also stimulate your immune system to fight viral warts. You may need to return to the clinic for repeat treatments every 2 to 3 weeks until the wart disappears.
Possible side effects of cryotherapy are pain, blisters and permanent changes in skin color (hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation), particularly in people with brown or Black skin.
-
Stronger peeling medicine (salicylic acid). Prescription-strength wart medications with salicylic acid work by removing a wart a layer at a time. They may also boost your immune system's ability to fight the wart.
Your health care provider will likely suggest you apply the medicine regularly at home, followed by occasional office visits. It might take weeks to remove the wart using this method.
Surgical or other procedures
If salicylic acid and freezing medicine don't work, your health care provider may suggest one or more of the following treatments:
- Minor surgery. Your health care provider cuts away the wart or destroys it by using an electric needle (electrodesiccation and curettage). This method can be painful, so your health care provider will numb your skin first. Because surgery has a risk of scarring, it's not often used to treat plantar warts unless other treatments have failed. A scar on the sole of the foot can be painful for years.
- Blistering medicine. Your health care provider applies cantharidin, which causes a blister under the wart. You may need to return to the clinic in about a week to have the dead wart clipped off.
- Immune therapy. This method uses medications or solutions to stimulate your immune system to fight viral warts. Your health care provider may inject your warts with a foreign substance (antigen) or apply a solution or cream to the warts.
- Laser treatment. Pulsed-dye laser treatment burns closed (cauterizes) tiny blood vessels. The infected tissue eventually dies, and the wart falls off. This method needs to be repeated every 2 to 4 weeks. Your health care provider will likely numb your skin first.
- Vaccine. HPV vaccine has been used with success to treat warts even though this vaccine is not specifically targeted toward the wart viruses that cause plantar warts.
If a plantar wart goes away after treatment and another wart grows, it could be because the area was exposed again to HPV.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Many people have removed warts with these self-care tips:
- Peeling medicine (salicylic acid). Nonprescription wart removal products are sold as a patch, gel or liquid. You'll likely be instructed to wash the site, soak it in warm water, and gently remove the top layer of softened skin with a pumice stone or emery board. Then after the skin has dried, you apply the solution or patch. Patches are often changed every 24 to 48 hours. Liquid products are used daily. It might take weeks to remove the wart using this method.
- Freezing medicine (cryotherapy). Nonprescription medicines that freeze the wart include Compound W Freeze Off and Dr. Scholl's Freeze Away. The Food and Drug Administration cautions that some wart removers are flammable and shouldn't be used around fire, flame, heat sources (such as curling irons) and lit cigarettes.
- Duct tape. Using duct tape to remove warts is a harmless but unproven approach. To try it, cover the wart with silver duct tape, changing it every few days. Between applications, soak the wart and gently remove dead tissue with a pumice stone or emery board. Then leave the wart open to the air to dry for a few hours before covering it with tape again.
In general, no matter which treatment you try, do these two things:
- Cover the wart to help prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body or to other people.
- Wash your hands after touching the wart.
If a plantar wart goes away after treatment and another wart grows, it could be because the area was exposed again to HPV.
Preparing for an appointment
You'll likely start by seeing your primary care provider, who may then refer you to a specialist in disorders of the skin (dermatologist) or feet (podiatrist). The following tips can help you prepare for your appointment.
Prevention
What you can do
Bring a list of all medications you take regularly — including nonprescription medications and dietary supplements — and the daily dosage of each.
You may also want to list questions for your health care provider, such as:
- If I have a plantar wart, can I start with at-home care?
- If I use a home treatment, under what conditions should I call you?
- If the first treatment doesn't work, what will we try next?
- If the growth isn't a plantar wart, what tests do you need to do?
- How long will it take to get results?
- How can I prevent warts?
Preparing for an appointment
What to expect from your doctor
Your health care provider may ask you questions such as:
- When did you first notice the wart?
- Has it changed in size, color or shape?
- Is your condition painful?
- Have you had warts before?
- Do you have diabetes or poor sensation in your feet?
- Do you have any condition or take any medication that has weakened your ability to fight disease (immune response)?
- Have you tried any home remedies? If so, how long have you used them and have they helped?
- Do you use a swimming pool or locker room — places that can harbor wart-causing viruses?
What you can do in the meantime
If you're sure you have a plantar wart, you may try nonprescription remedies or alternative medicine approaches. But talk with your health care provider before trying self-care treatments if you have:
- Diabetes
- Poor sensation in your feet
- Weakened immunity
If pressure on the wart causes pain, try wearing well-cushioned shoes, such as athletic shoes that evenly support the sole and relieve some of the pressure. Avoid wearing uncomfortable shoes.
© 1998-2025 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). All rights reserved. Terms of Use


