Overview
Epilepsy — also known as a seizure disorder — is a brain condition that causes recurring seizures. There are many types of epilepsy. In some people, the cause can be identified. In others, the cause is not known.
Epilepsy is common. It's estimated that 1.2% of people in the United States have active epilepsy, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Epilepsy affects people of all genders, races, ethnic backgrounds and ages.
Seizure symptoms can vary widely. Some people may lose awareness during a seizure while others don't. Some people stare blankly for a few seconds during a seizure. Others may repeatedly twitch their arms or legs, movements known as convulsions.
Having a single seizure doesn't mean you have epilepsy. Epilepsy is diagnosed if you've had at least two unprovoked seizures at least 24 hours apart. Unprovoked seizures don't have a clear cause.
Treatment with medicines or sometimes surgery can control seizures for most people with epilepsy. Some people require lifelong treatment. For others, seizures go away. Some children with epilepsy may outgrow the condition with age.
Symptoms
Seizure symptoms vary depending on the type of seizure. Because epilepsy is caused by certain activity in the brain, seizures can affect any brain process. Seizure symptoms may include:
- Temporary confusion.
- A staring spell.
- Stiff muscles.
- Uncontrollable jerking movements of the arms and legs.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Psychological symptoms such as fear, anxiety or deja vu.
Sometimes people with epilepsy may have changes in their behavior. They also may have symptoms of psychosis.
Most people with epilepsy tend to have the same type of seizure each time. Symptoms are usually similar from episode to episode.
Warning signs of seizures
Some people with focal seizures have warning signs in the moments before a seizure begins. These warning signs are known as aura.
Warning signs might include a feeling in the stomach. Or they might include emotions such as fear. Some people might feel deja vu. Auras also might be a taste or a smell. They might even be visual, such as a steady or flashing light, a color, or a shape. Some people may experience dizziness and loss of balance. And some people may see things that aren't there, known as hallucinations.
Seizures are classified as either focal or generalized, based on how and where the brain activity causing the seizure begins.
When seizures appear to result from activity in just one area of the brain, they're called focal seizures. These seizures fall into two categories:
- Focal seizures without loss of consciousness. Once called simple partial seizures, these seizures don't cause a loss of awareness, also known as consciousness. They may alter emotions or change the way things look, smell, feel, taste or sound. Some people experience deja vu. This type of seizure also may result in involuntary jerking of a body part, such as an arm or a leg. And focal seizures may cause sensory symptoms such as tingling, dizziness and flashing lights.
- Focal seizures with impaired awareness. Once called complex partial seizures, these seizures involve a change or loss of consciousness. This type of seizure may seem like being in a dream. During a focal seizure with impaired awareness, people may stare into space and not respond in typical ways to the environment. They also may perform repetitive movements, such as hand rubbing, chewing, swallowing or walking in circles.
Symptoms of focal seizures may be confused with other neurological conditions, such as migraine, narcolepsy or mental illness. A thorough exam and testing are needed to tell if symptoms are the result of epilepsy or another condition.
Focal seizures may come from any lobe of the brain. Some types of focal seizures include:
- Temporal lobe seizures. Temporal lobe seizures begin in the areas of the brain called the temporal lobes. The temporal lobes process emotions and play a role in short-term memory. People who have these seizures often experience an aura. The aura may include sudden emotion such as fear or joy. It also may be a sudden taste or smell. Or an aura may be a feeling of deja vu, or a rising sensation in the stomach. During the seizure, people may lose awareness of their surroundings. They also may stare into space, smack their lips, swallow or chew repeatedly, or have movements of their fingers.
- Frontal lobe seizures. Frontal lobe seizures begin in the front of the brain. This is the part of the brain that controls movement. Frontal lobe seizures cause people to move their heads and eyes to one side. They won't respond when spoken to and may scream or laugh. They might extend one arm and flex the other arm. They also might make repetitive movements such as rocking or bicycle pedaling.
- Occipital lobe seizures. These seizures begin in the area of the brain called the occipital lobe. This lobe affects vision and how people see. People who have this type of seizure may have hallucinations. Or they may lose some or all of their vision during the seizure. These seizures also might cause eye blinking or make the eyes move.
Generalized seizures
Seizures that appear to involve all areas of the brain are called generalized seizures. Generalized seizures include:
- Absence seizures. Absence seizures, previously known as petit mal seizures, typically occur in children. Symptoms include staring into space with or without subtle body movements. Movements may include eye blinking or lip smacking and only last 5 to 10 seconds. These seizures may occur in clusters, happening as often as 100 times a day, and cause a brief loss of awareness.
- Tonic seizures. Tonic seizures cause stiff muscles and may affect consciousness. These seizures usually affect muscles in the back, arms and legs and may cause the person to fall to the ground.
- Atonic seizures. Atonic seizures, also known as drop seizures, cause a loss of muscle control. Since this most often affects the legs, it often causes sudden falls to the ground.
- Clonic seizures. Clonic seizures are associated with repeated or rhythmic jerking muscle movements. These seizures usually affect the neck, face and arms.
- Myoclonic seizures. Myoclonic seizures usually appear as sudden brief jerks or twitches and usually affect the upper body, arms and legs.
- Tonic-clonic seizures. Tonic-clonic seizures, previously known as grand mal seizures, are the most dramatic type of epileptic seizure. They can cause a sudden loss of consciousness and body stiffening, twitching and shaking. They sometimes cause loss of bladder control or biting of the tongue.
When to see a doctor
Seek immediate medical help if any of the following occurs with a seizure:
- The seizure lasts more than five minutes.
- Breathing or consciousness doesn't return after the seizure stops.
- A second seizure follows immediately.
- You have a high fever.
- You're pregnant.
- You have diabetes.
- You've injured yourself during the seizure.
- You continue to have seizures even though you've been taking anti-seizure medicine.
If you have a seizure for the first time, seek medical advice.
Causes
Epilepsy has no identifiable cause in about half the people with the condition. In the other half, the condition may be traced to various factors, including:
-
Genetic influence. Some types of epilepsy run in families. In these instances, it's likely that there's a genetic influence. Researchers have linked some types of epilepsy to specific genes. But some people have genetic epilepsy that isn't hereditary. Genetic changes can occur in a child without being passed down from a parent.
For most people, genes are only part of the cause of epilepsy. Certain genes may make a person more sensitive to environmental conditions that trigger seizures.
- Head trauma. Head trauma as a result of a car accident or other traumatic injury can cause epilepsy.
- Factors in the brain. Brain tumors can cause epilepsy. Epilepsy also may be caused by the way blood vessels form in the brain. People with blood vessel conditions such as arteriovenous malformations and cavernous malformations can have seizures. And in adults older than age 35, stroke is a leading cause of epilepsy.
- Infections. Meningitis, HIV, viral encephalitis and some parasitic infections can cause epilepsy.
- Injury before birth. Before they're born, babies are sensitive to brain damage that could be caused by several factors. They might include an infection in the mother, poor nutrition or not enough oxygen. This brain damage can result in epilepsy or cerebral palsy.
- Developmental conditions. Epilepsy can sometimes occur with developmental conditions. People with autism are more likely to have epilepsy than are people without autism. Research also has found that people with epilepsy are more likely to have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other developmental conditions. Having both conditions may be related to genes.
Seizure triggers
Seizures can be triggered by things in the environment. Seizure triggers don't cause epilepsy, but they may trigger seizures in people who have epilepsy. Most people with epilepsy don't have reliable triggers that always cause a seizure. However, they often can identify factors that make it easier to have a seizure. Possible seizure triggers include:
- Alcohol.
- Flashing lights.
- Illicit drug use.
- Skipping doses of antiseizure medicines or taking more than prescribed.
- Lack of sleep.
- Hormone changes during the menstrual cycle.
- Stress.
- Dehydration.
- Skipped meals.
- Illness.
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase your risk of epilepsy:
- Age. The onset of epilepsy is most common in children and older adults, but the condition can occur at any age.
- Family history. If you have a family history of epilepsy, you may be at an increased risk of seizures.
- Head injuries. Head injuries are responsible for some cases of epilepsy. You can reduce your risk by wearing a seat belt while riding in a car. Also wear a helmet while bicycling, skiing, riding a motorcycle or doing any activities with a high risk of head injury.
- Stroke and other vascular diseases. Stroke and other blood vessel diseases can cause brain damage. Brain damage may trigger seizures and epilepsy. You can take steps to reduce your risk of these diseases. Limit alcohol, don't smoke, eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Dementia. Dementia can increase the risk of epilepsy in older adults.
- Brain infections. Infections such as meningitis, which causes inflammation in the brain or spinal cord, can increase your risk.
- Seizures in childhood. High fevers in childhood can sometimes be associated with seizures. Children who have seizures due to high fevers generally won't develop epilepsy. The risk of epilepsy increases if a child has a long fever-associated seizure, another nervous system condition or a family history of epilepsy.
Complications
Having a seizure at certain times can be dangerous to yourself or others.
- Falling. If you fall during a seizure, you can injure your head or break a bone.
- Drowning. People with epilepsy are 13 to 19 times more likely to drown while swimming or bathing than people without epilepsy. The risk is higher because you might have a seizure while in the water.
-
Car accidents. A seizure that causes either loss of awareness or control can be dangerous if you're driving a car or operating other equipment.
Many states have driver's license restrictions related to a driver's ability to control seizures. In these states, there is a minimum amount of time that a driver must be seizure-free before being cleared to drive. The amount of time may range from months to years.
- Trouble with sleep. People who have epilepsy may have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, known as insomnia.
-
Pregnancy complications. Seizures during pregnancy pose dangers to both mother and baby. Also, certain anti-seizure medicines increase the risk of birth defects. If you have epilepsy and you're considering becoming pregnant, get medical help as you plan your pregnancy.
Most women with epilepsy can become pregnant and have healthy babies. You need to be carefully monitored throughout pregnancy. Your medicines may need to be adjusted. It's very important that you work with your healthcare team to plan your pregnancy.
- Memory loss. People with some types of epilepsy have trouble with memory.
Emotional health issues
People with epilepsy are more likely to have mental health conditions. They may be a result of dealing with the condition itself as well as medicine side effects. But even people with well-controlled epilepsy are at increased risk. Emotional health problems that may affect people with epilepsy include:
- Depression.
- Anxiety.
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Other life-threatening complications of epilepsy are not common but may happen. These include:
- Status epilepticus. This condition occurs if you're in a state of continuous seizure activity lasting more than five minutes. Or it may occur if you have seizures without regaining full consciousness in between them. People with status epilepticus have an increased risk of permanent brain damage and death.
-
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). People with epilepsy also have a small risk of sudden unexpected death. The cause is unknown, but some research shows that it may occur due to heart or respiratory conditions.
People with frequent tonic-clonic seizures or people whose seizures aren't controlled by medicines may be at higher risk of SUDEP. Overall, about 1% of people with epilepsy die of SUDEP. It's most common in those with severe epilepsy that doesn't respond to treatment.
Diagnosis
To diagnose epilepsy, your healthcare professional reviews your symptoms and medical history. You may have several tests to diagnose epilepsy and to detect the cause of seizures. They may include:
- A neurological exam. This exam tests your behavior, movements, mental function and other areas. The exam helps diagnose epilepsy and determine the type of epilepsy you may have.
- Blood tests. A blood sample can detect signs of infections, genetic conditions or other conditions that may be associated with seizures.
- Genetic testing. In some people with epilepsy, genetic testing may give more information about the condition and how to treat it. Genetic testing is most often performed in children but also may be helpful in some adults with epilepsy.
You also may have brain imaging tests and scans that detect brain changes:
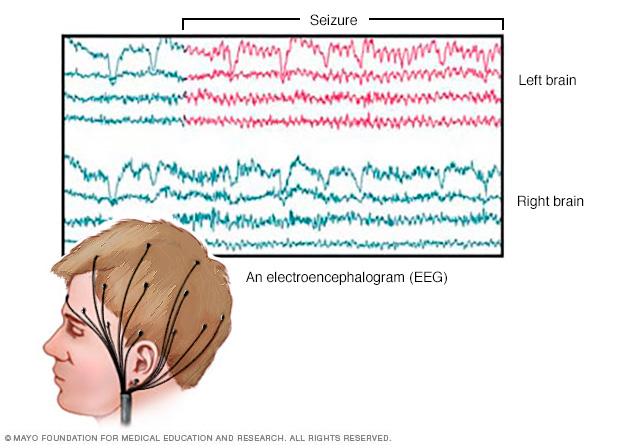
Electroencephalogram (EEG). This is the most common test used to diagnose epilepsy. In this test, small metal discs called electrodes are attached to your scalp with an adhesive or cap. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain.
If you have epilepsy, it's common to have changes in the pattern of brain waves. These changes occur even when you're not having a seizure. Your healthcare professional may monitor you on video during an EEG to detect and record any seizures. This may be done while you're awake or asleep. Recording the seizures may help determine what kind of seizures you're having or rule out other conditions.
The test may be done in a healthcare professional's office or the hospital. Or you may have an ambulatory EEG. The EEG records seizure activity over the course of a few days at home.
You may get instructions to do something that can cause seizures, such as getting little sleep prior to the test.
- High-density EEG. In a variation of an EEG test, you may have a high-density EEG. For this test, electrodes are placed closer together compared with a conventional EEG. High-density EEG may help more precisely determine which areas of your brain are affected by seizures.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan. A CT scan uses X-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of your brain. CT scans can detect tumors, bleeding or cysts in the brain that might be causing epilepsy.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create a detailed view of the brain. Like a CT scan, an MRI looks at the structure of the brain to detect what may be causing seizures. But an MRI provides a more detailed look at the brain than a CT scan.
- Functional MRI (fMRI). A functional MRI measures the changes in blood flow that occur when specific parts of the brain are working. This test may be used before surgery to identify the exact locations of critical functions, such as speech and movement. This allows surgeons to avoid those areas while operating.
- Positron emission tomography (PET). PET scans use a small amount of low-dose radioactive material. The material is injected into a vein to help visualize metabolic activity of the brain and detect changes. Areas of the brain with low metabolism may indicate places where seizures occur.
-
Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT). This type of test is used if MRI and EEG didn't pinpoint the location in the brain where the seizures start.
A SPECT test uses a small amount of low-dose radioactive material. The material is injected into a vein to create a detailed, 3D map of blood flow during seizures. Areas of higher than typical blood flow may indicate areas where seizures occur.
Another type of SPECT test called subtraction ictal SPECT coregistered to MRI (SISCOM) may provide even more-detailed results. The test overlaps the SPECT results with brain MRI results.
- Neuropsychological tests. These tests assess thinking, memory and speech skills. The test results help determine which areas of the brain are affected by seizures.
Along with your test results, a combination of other techniques may be used to help pinpoint where in the brain seizures start:
- Statistical parametric mapping (SPM). SPM looks at the areas of the brain with increased blood flow during seizures. It's compared to the same areas of the brains of people who don't have seizures. This provides information about where seizures begin.
- Electrical source imaging (ESI). ESI is a technique that takes EEG data and projects it onto an MRI of the brain. This is done to show areas where seizures are occurring. This technique provides more-precise detail than does EEG alone.
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG). MEG measures the magnetic fields produced by brain activity. This helps find the potential areas where seizures start. MEG can be more accurate than EEG because the skull and tissue surrounding the brain interfere less with magnetic fields. MEG and MRI together provide images that show areas of the brain both affected by seizures and not affected by seizures.
Diagnosis of your seizure type and where seizures begin gives you the best chance for finding an effective treatment.
Treatment
Treatment can help people diagnosed with epilepsy have fewer seizures or even completely stop having seizures. Possible treatments include:
- Medicines.
- Surgery.
- Therapies that stimulate the brain using a device.
- A ketogenic diet.
Medication
Most people with epilepsy can become seizure-free by taking one anti-seizure medicine, which is also called an anti-epileptic medicine. Others may be able to decrease the number and intensity of their seizures by taking more than one medicine.
Many children with epilepsy who aren't having epilepsy symptoms can eventually stop taking medicines and live a seizure-free life. Many adults can stop taking medicines after two or more years without seizures. Your healthcare team can advise you about the appropriate time to stop taking medicines.
Finding the right medicine and dosage can be complex. Your provider may consider your condition, how often you have seizures, your age and other factors when choosing which medicine to prescribe. Your provider also may review any other medicines you may be taking to ensure the anti-seizure medicines won't interact with them.
You may first take a single medicine at a low dose. Then your healthcare professional may increase the dosage gradually until your seizures are well controlled.
There are more than 20 different types of anti-seizure medicines available. The medicines that you take depend on the type of seizures you have, your age and other health conditions.
Anti-seizure medicines may have some side effects. Mild side effects include:
- Fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Weight gain.
- Loss of bone density.
- Skin rashes.
- Loss of coordination.
- Speech problems.
- Memory and thinking problems.
More-serious but rare side effects include:
- Depression.
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
- Severe rash.
- Inflammation of certain organs, such as the liver.
For the best seizure control possible with medicine, follow these steps:
- Take medicines exactly as prescribed.
- Always call your healthcare professional before switching to a generic version of your medicine or taking other medicines. This includes medicines you get with or without a prescription and herbal remedies.
- Never stop taking your medicine without talking to your healthcare professional.
- Tell your healthcare professional immediately if you notice new or increased feelings of depression or suicidal thoughts. Also contact your healthcare professional right away if you have changes in your mood or behaviors.
- Tell your healthcare professional if you have migraines. You may need an anti-seizure medicine that can prevent your migraines and treat epilepsy.
At least half the people newly diagnosed with epilepsy become seizure-free with their first medicine. If anti-seizure medicines don't provide good results, you may be able to have surgery or other therapies. You'll likely have regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to check on your condition and medicines.
Surgery
When medicines do not provide enough control of seizures, epilepsy surgery may be an option. With epilepsy surgery, a surgeon removes the area of your brain that's causing seizures.
Surgery usually is done when tests show that:
- Your seizures start in a small, well-defined area of your brain.
- The surgery wouldn't affect vital functions such as speech, language, movement, vision or hearing.
For some types of epilepsy, minimally invasive approaches such as MRI-guided stereotactic laser ablation may help symptoms. These treatments may be used when open surgery is too risky. This procedure involves using a thermal laser probe directed at the area in the brain causing seizures. It destroys tissue in an effort to better control the seizures.
You may continue to take medicine to help prevent seizures after successful surgery. However, you may be able to take fewer medicines and reduce your doses.
In a small number of people, surgery for epilepsy can cause complications. Complications may include a permanent change in thinking abilities. Talk to your surgical team members about their experience, success rates and complication rates with the procedure you're considering.
Therapies
Apart from medicines and surgery, these potential therapies offer an alternative for treating epilepsy:
-
Vagus nerve stimulation. Vagus nerve stimulation may be an option when medicines haven't worked well enough to control seizures and surgery isn't possible. A device called a vagus nerve stimulator is implanted underneath the skin of the chest, similar to a heart pacemaker. Wires from the stimulator are connected to the vagus nerve in the neck.
The battery-powered device sends bursts of electrical energy through the vagus nerve and to the brain. It's not clear how this inhibits seizures, but the device can usually reduce seizures by 20% to 40%.
Most people still need to take anti-seizure medicine. But some people may be able to lower their medicine dose. Vagus nerve stimulation side effects may include throat pain, hoarse voice, shortness of breath or coughing.
- Deep brain stimulation. In deep brain stimulation, surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of the brain, typically the thalamus. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in the chest. The generator regularly sends electrical pulses to the brain at timed intervals and may reduce seizures. Deep brain stimulation is often used for people whose seizures don't get better with medicine.
- Responsive neurostimulation. These implantable, pacemaker-like devices can help reduce how often seizures occur. The devices analyze brain activity patterns to detect seizures as they start. They deliver electrical stimulation to stop the seizure. Research shows that this therapy has few side effects and can provide long-term seizure relief.
Ketogenic diet
Some children and adults with epilepsy reduce their seizures by following a diet high in fats and low in carbohydrates. This may be an option when medicines aren't helping to control epilepsy.
In this diet, called a ketogenic diet, the body breaks down fats instead of carbohydrates for energy. After a few years, some children may be able to stop the ketogenic diet and remain seizure-free. It's important for this to be done under close supervision of healthcare professionals.
Experts don't fully know how a ketogenic diet works to reduce seizures. But researchers think that the diet creates chemical changes that suppress seizures. The diet also alters the actions of brain cells to reduce seizures.
Get medical advice if you or your child is considering a ketogenic diet. It's important to make sure that your child gets enough nutrients when following the diet.
Side effects of a ketogenic diet may include dehydration, constipation and slowed growth from not getting enough nutrition. Side effects also may include a buildup of uric acid in the blood, which can cause kidney stones. These side effects are not common if the diet is properly and medically supervised.
Following a ketogenic diet can be hard. Low-glycemic index and modified Atkins diets offer less restrictive alternatives that may still provide some help for seizure control.
Potential future treatments
Researchers are studying many potential new treatments for epilepsy, including:
-
Continuous stimulation of the seizure onset zone, known as subthreshold stimulation. Subthreshold stimulation is continuous stimulation to an area of the brain below a level that's physically noticeable. This type of therapy appears to improve seizure outcomes and quality of life for some people with seizures. Subthreshold stimulation helps stop a seizure before it happens.
This treatment may work in people who have seizures that start in an area of the brain called the eloquent area. This area can't be removed because it would affect speech and movements. Or it might help people with seizure types that may not improve with responsive neurostimulation.
- Minimally invasive surgery. New minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as MRI-guided focused ultrasound, show promise for treating seizures. These surgeries have fewer risks than traditional open-brain surgery for epilepsy.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). TMS applies focused magnetic fields on areas of the brain where seizures occur to treat seizures without the need for surgery. It may be used for patients whose seizures occur close to the surface of the brain and can't be treated with surgery.
- Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). This technique provides electrical stimulation through the scalp to the brain to reduce seizures over time. This treatment may be provided at home.

Lifestyle and home remedies
Understanding your condition can help you take better control of it:
- Take your medicine correctly. Don't adjust your dosage before talking to a member of your healthcare team. If you feel that your medicine should be changed, talk with your healthcare professional.
- Get enough sleep. Lack of sleep can trigger seizures. Be sure to get adequate rest every night.
- Wear a medical alert bracelet. This will help emergency staff know how to treat you correctly.
- Exercise. Exercising may help keep you physically healthy and reduce depression. Make sure to drink enough water, and rest if you get tired during exercise.
In addition, make healthy life choices. Manage stress, limit alcohol and don't smoke cigarettes.
Coping and support
Not being able to control seizures can lead to depression. But you can live an active, full life with epilepsy. To help cope:
- Educate yourself and your friends and family about epilepsy so that they understand the condition.
- Try to ignore negative reactions from people. It helps to learn about epilepsy so that you know the facts as opposed to misconceptions about the disease. And try to keep your sense of humor.
- Live as independently as possible. Continue to work, if possible. If you can't drive because of your seizures, investigate public transportation options near you. If you are not cleared to drive, you might consider moving to a city with good public transportation options.
- Find a healthcare professional you like and with whom you feel comfortable.
- Try not to worry about having a seizure.
- Find an epilepsy support group to meet people who understand what you're going through.
If you can't work outside of the home because of your seizures, you might consider working from home. And there are other ways to feel connected to people.
Let people you work and live with know how to handle a seizure. This can help if they are with you when you have one. You may offer them suggestions such as:
- Carefully roll the person onto one side to prevent choking.
- Place something soft under the person's head.
- Loosen tight neckwear.
- Don't place fingers or anything else in the person's mouth. People with epilepsy will not "swallow" their tongues during a seizure — it's physically impossible.
- Don't try to restrain someone having a seizure.
- If the person is moving, clear away dangerous objects.
- If immediate medical help is needed, stay with the person until medical staff arrive.
- Observe the person closely so that you can provide details on what happened.
- Time the seizures.
- Be calm during the seizures.
Preparing for an appointment
You may start by seeing your healthcare professional. However, when you call to set up an appointment, you may be referred immediately to a specialist. This specialist may be a doctor trained in brain and nervous system conditions, known as a neurologist. Or you may be referred to a neurologist trained in epilepsy, known as an epileptologist.
Appointments can be brief and there's often a lot to talk about. It's a good idea to be well prepared. Here's information to help you get ready for your appointment, and what to expect.
What you can do
-
Keep a detailed seizure calendar. Each time a seizure occurs, write down the time, the type of seizure and how long it lasted. Also make note of any circumstances surrounding the seizure. They might include missed medicines, lack of sleep, increased stress, menstruation or other events that might trigger seizure activity.
Seek input from people who may observe your seizures, including family, friends and co-workers. It allows you to record information you may not know.
- Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions. At the time you make the appointment, ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as restrict your diet.
- Write down key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes.
- Make a list of all medicines, vitamins or supplements that you're taking.
-
Take a family member or friend along. Sometimes it can be difficult to remember all the information provided to you during an appointment. Someone who comes with you may remember something that you missed or forgot.
You may not be aware of everything that happens when you're having a seizure. Someone else who has seen your seizures may be able to answer questions during your appointment.
- Write down questions to ask your healthcare professional. Preparing a list of questions helps you make the most of your appointment time.
For epilepsy, some basic questions include:
- What is likely causing my seizures?
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- Is my epilepsy likely temporary or long-lasting?
- What treatment do you recommend?
- What are the alternatives to the primary treatment that you're suggesting?
- How can I make sure that I don't hurt myself if I have another seizure?
- I have these other health conditions. How can I best manage them together?
- Are there any restrictions that I need to follow?
- Should I see a specialist? What will that cost, and will my insurance cover it?
- Is there a generic alternative to the medicine you're prescribing?
- Are there any brochures or other printed material that I can take home with me? What websites do you recommend?
In addition to the questions that you've prepared, don't hesitate to ask questions during your appointment at any time that you don't understand something.
What to expect from your doctor
Your healthcare professional is likely to ask you a number of questions, such as:
- When did you first begin experiencing seizures?
- Do your seizures seem to be triggered by certain events or conditions?
- Do you have similar sensations just before the onset of a seizure?
- Have your seizures occurred often or occasionally?
- What symptoms do you have when you experience a seizure?
- What, if anything, seems to improve your seizures?
- What, if anything, appears to worsen your seizures?
What you can do in the meantime
Certain conditions and activities can trigger seizures, so it may be helpful if you:
- Don't drink large amounts of alcohol.
- Don't use nicotine.
- Get enough sleep.
- Reduce stress.
Also, it's important to keep a log of your seizures before your appointment.
© 1998-2025 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). All rights reserved. Terms of Use


